In this Article

What Is a Radiology Technologist?
A radiology technician, also known as a radiologic technologist or radiographer, specializes in performing diagnostic imaging procedures on patients. They utilize various techniques, including X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), to create detailed diagnostic images that aid in the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions.
How to Become a Radiology Technologist
These steps can guide you as you pursue your education.
Earn your high school diploma or GED.

You’ll need a high school education to apply to radiology technology programs.
Earn a degree.

You can choose from a certificate, associate degree, or bachelor’s degree in radiology technology.
Earn certification.
You’ll need to attend an accredited program to earn certification, which most states and employers will require.
Consider specializing.

As a radiology technician, you’ll likely start your career taking X-rays. But there are many specialty certifications that will qualify you to branch out into other imaging procedures, including sonography, MRI, and mammography.
What You’ll Do
Radiology technologists—also known as radiologic technologists, radiographers, and X-ray technologists—play a key role in helping to identify conditions such as cancer, ulcers, or broken bones. As a radiology technologist, you’ll need to be aware of radiation safety measures and protection to comply with government regulations and ensure the safety of patients and yourself.
As your experience grows and you earn professional certifications, your opportunities may increase, allowing you to enter a job market for radiology techs that is consistent with the national growth for all professions.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), jobs for radiology technologists are expected to grow by 5.5% through 2032, in line with the growth projected for all other occupations combined. This means that now could be a promising time to become a radiology tech.
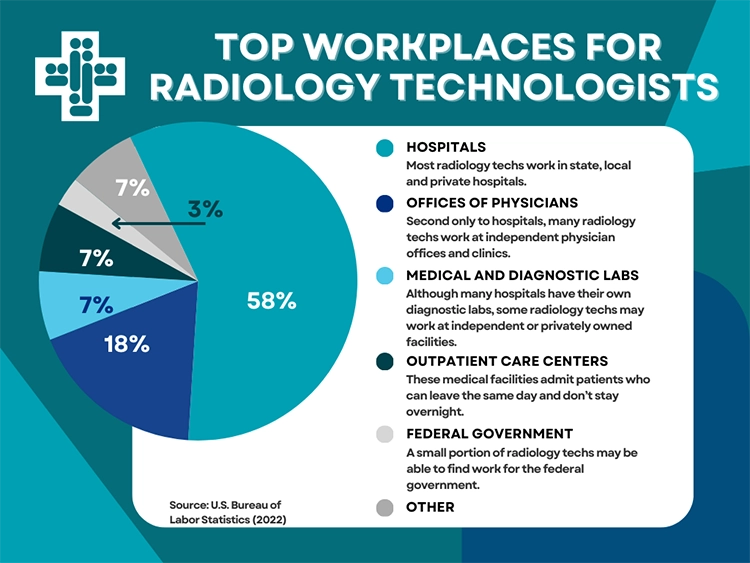
Where Radiology Techs Work
The majority of radiology technologists work in hospitals. Here are some common workplaces and the percentage of technologists they employ, according to the BLS.
Education Requirements
There are formal education programs in radiography that lead to a certificate, associate degree, or a bachelor’s degree. The associate degree program is the most common. It takes about two years to complete, while a bachelor’s degree usually takes four years.
Both programs include classroom and clinical training. You can expect to study these subjects:
One thing to consider when choosing any school and program is accreditation, which is a seal of approval for your curriculum. Accredited schools have been reviewed by professional associations, subject matter experts, and regional accreditation agencies to make sure they provide a quality education.
The Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiologic Technology (JRCERT) accredits educational and training programs in radiography.
Certificate vs Certification
- Certificate
- A certificate is awarded by an educational institution, and signifies that a student has satisfactorily completed a given curriculum. Certificate programs can help students prepare for certification exams.
- Certification
- A certification is generally awarded by a trade group after an individual has met certain professional requirements (e.g. earned a specific degree, worked professionally in a given field for a set amount of time, etc.) and passed a certification exam.
In short, a certificate is evidence that someone has completed an educational program, while a certification denotes that someone has met a certain set of professional criteria and/or passed an exam.
Not all programs offered are designed to meet state educator licensing or advancement requirements; however, it may assist candidates in gaining these approvals in their state of residence depending on those requirements. Contact the state board of education in the applicable state(s) for requirements.
Radiology Technologist Personality Traits and Skills
Radiology technologists work with patients who may be anxious or fearful about imaging procedures or their current health concerns. Being able to help patients move through a procedure with as much ease as possible is the mark of a good radiology tech.
These personality traits and skills may help you succeed as a radiology technologist.
You are:
- An active listener
- Compassionate
- A clear communicator
- Comfortable working with the public
- A problem solver
You have:
- Excellent customer service skills
- Time management skills
- A knack for critical thinking
- Patience
- Attention to detail
Salary
According to the BLS 2023 data, the median annual salary for radiology technologists is $73,410.
Salaries can range depending on where you work, however. The top 10% of radiology technologists earn more than $102,380, with the highest earners typically working in outpatient care centers, according to the BLS.
Licensing and Certification
Most states require radiology technologists to be licensed, and the vast majority require them to earn the certification Registered Radiologic Technologist R.T. (R). This requires graduating from an accredited program and passing a certification exam given by the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT).
As a rule, employers expect job candidates to have the R.T. (R) certification, so it’s a good idea to plan on pursuing this credential.
To maintain their certification, radiologic technologists must complete 24 hours of continuing education every two years. This education could include online classes, self-study readings, lectures at professional society meetings, and classroom learning.
As you build your career, certifications can help you specialize in a specific type of imaging, such as nuclear medicine or ultrasound.
Here are some of the certifications available to radiology technologists as they gain experience:
Nuclear Medicine Technology (N)
Sonography (S)
Computed Tomography (CT)
Mammography (M)
Written and reported by:
All Star Directories Staff